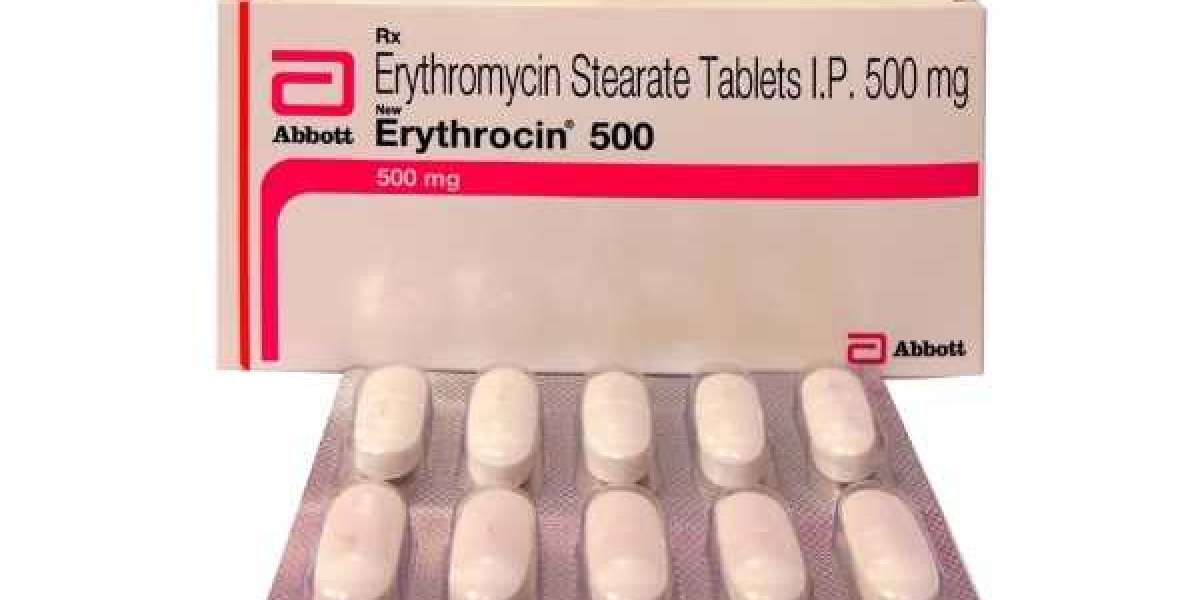
Understanding Erythromycin:
Erythromycin is primarily known as an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. However, it also possesses certain properties that make it potentially useful in managing coughs. As a macrolide antibiotic, erythromycin exhibits anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects, which can help reduce airway inflammation and cough severity.
Erythromycin's Mechanism of Action:
Erythromycin works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, leading to their death or inhibition of growth. However, its effects on cough are not solely related to its antibiotic properties. Erythromycin also acts as a motilin receptor agonist, stimulating the contraction of smooth muscles in the respiratory tract and enhancing clearance of mucus and irritants.
Effectiveness of Erythromycin for Cough:
While erythromycin's use in managing cough is not its primary indication, some studies have explored its potential benefits. It has shown promise in certain conditions where cough is a prominent symptom, such as pertussis (whooping cough) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Erythromycin's anti-inflammatory and motility-enhancing properties can help reduce cough frequency and improve mucus clearance in these cases.
However, it's important to note that erythromycin may not be effective for all types of cough. Coughs caused by viral infections or allergies, for instance, may not benefit significantly from erythromycin treatment. It is crucial to determine the underlying cause of the cough through proper medical evaluation and diagnosis.
Dosage and Administration:
The dosage and duration of erythromycin treatment for cough will depend on the specific condition being treated and the healthcare provider's recommendations. It is typically taken orally, either with or without food, as directed by the prescribing physician. Adhering to the prescribed dosage and completing the full course of treatment is essential to achieve optimal results.
Precautions and Side Effects:
Like any medication, erythromycin carries the risk of side effects. Common side effects may include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. Allergic reactions and interactions with other medications are also possible. It is important to discuss your medical history, current medications, and any known allergies with your healthcare provider before starting erythromycin.
Conclusion:
While erythromycin 500 may offer potential benefits in managing certain cough conditions, its use should be based on a proper diagnosis and healthcare professional's recommendation. It is not a first-line treatment for all types of coughs, and the underlying cause needs to be considered. If you are experiencing a persistent or severe cough, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider who can assess your symptoms, perform necessary tests, and recommend the most appropriate treatment for your specific condition.
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment recommendations.