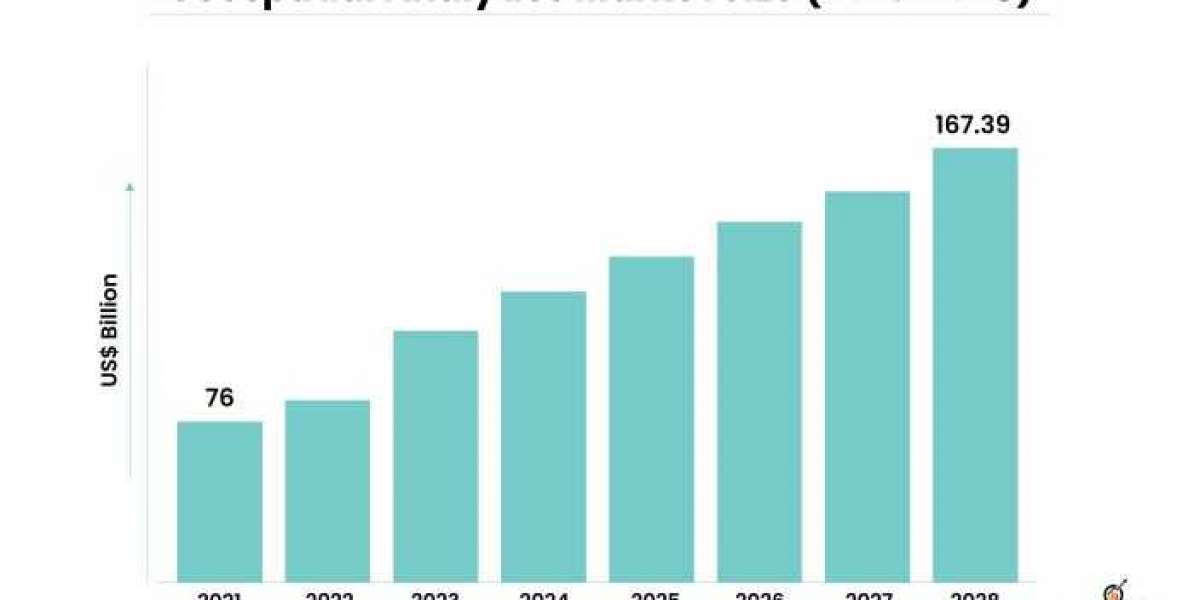
Urbanization is an unstoppable global trend, with an ever-increasing number of people moving to cities in search of better opportunities and improved living standards. This rapid urban growth poses significant challenges to city planners, demanding innovative and sustainable solutions to create smart, efficient, and livable urban spaces. Geospatial analytics, a revolutionary technology that harnesses the power of data and spatial analysis, has emerged as a crucial tool in urban planning and the development of smart cities. This article delves into the impact of geospatial analytics in shaping the urban landscape and fostering smart cities of the future. The geospatial analytics market is projected to grow from USD 76 billion in 2021 to USD 167.39 billion by 2028 at a CAGR of 11.78% during the forecast period.
What is Geospatial Analytics?
Geospatial analytics is the process of gathering, manipulating, and interpreting data related to geographic locations. It involves integrating various data sources, such as satellite imagery, aerial photographs, GPS data, and IoT sensors, to derive valuable insights about the physical and social aspects of a location. The combination of geospatial data with advanced analytical techniques, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, allows urban planners to make informed decisions and design cities that are more efficient, sustainable, and resilient.
Enhanced Urban Planning and Infrastructure Development
Traditional urban planning often relied on static maps and limited data sources, which made it challenging to consider the dynamic nature of cities. Geospatial analytics provides real-time and comprehensive data on traffic patterns, population density, land use, and environmental conditions. With this information, planners can optimize the placement of infrastructure, such as roads, public transportation, and utilities, to improve accessibility and reduce congestion.
Furthermore, geospatial analytics aids in identifying areas prone to natural disasters, enabling better disaster preparedness and response strategies. It allows planners to create resilient urban infrastructure that can withstand the impact of floods, earthquakes, and other calamities, safeguarding the lives and property of city residents.
Efficient Resource Management
In smart cities, resource management is a critical aspect of ensuring sustainability and minimizing waste. Geospatial analytics helps monitor and manage resources such as energy, water, and waste more effectively. For instance, by analyzing energy consumption patterns, cities can implement demand-based energy distribution systems and optimize power usage, leading to reduced carbon emissions and lower utility costs.
Water management is another area where geospatial analytics plays a vital role. By monitoring water sources, detecting leaks, and analyzing consumption patterns, cities can conserve water and improve water distribution, ensuring a sustainable water supply for residents.
Empowering Citizen Engagement
Geospatial analytics fosters transparency and public participation in urban planning. Smart city initiatives often involve citizen-centric approaches, where the input and feedback from residents are crucial in decision-making processes. By providing accessible and interactive maps, geospatial analytics allows citizens to understand urban development projects better and voice their opinions effectively.
Citizens can use geospatial data platforms to report issues such as potholes, damaged infrastructure, or environmental concerns. This real-time feedback enables authorities to respond promptly, enhancing the overall efficiency and responsiveness of city governance.
Improving Transportation and Mobility
Traffic congestion is a major challenge in urban areas, leading to increased travel time, air pollution, and reduced productivity. Geospatial analytics aids in developing intelligent transportation systems by collecting data from GPS devices, sensors, and traffic cameras. This data is then used to analyze traffic patterns, identify bottlenecks, and optimize traffic flow.
Smart cities utilize geospatial analytics to implement dynamic traffic management systems, real-time navigation apps, and smart parking solutions. These advancements not only reduce congestion but also promote the use of public transportation, cycling, and walking, thereby improving air quality and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Conclusion
Geospatial analytics has emerged as a powerful tool in transforming urban planning and driving the development of smart cities. By harnessing the wealth of spatial data, cities can make informed decisions, enhance infrastructure, optimize resource management, and improve the overall quality of life for their residents. As technology continues to evolve, the potential of geospatial analytics in shaping the urban landscape and fostering sustainable smart cities is limitless. Embracing these advancements will be crucial in creating a future where cities are not only connected and efficient but also sustainable and resilient to the challenges of a rapidly urbanizing world.