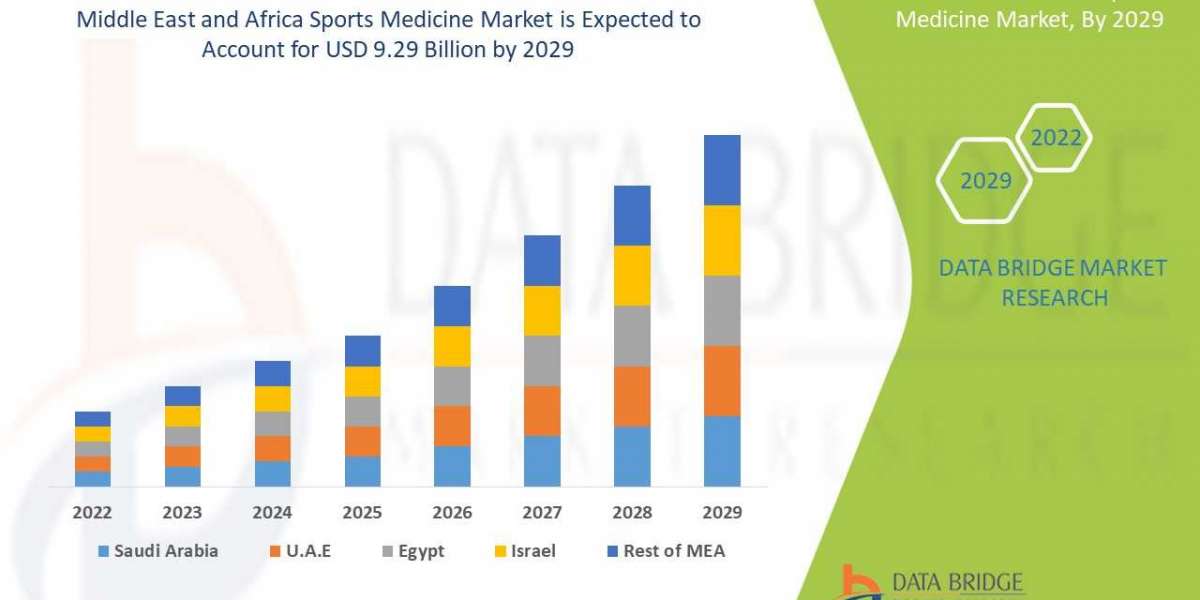
The "One Belt, One Road 138" (OBOR138) initiative, also known as the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), is one of China's most ambitious and far-reaching projects aimed at enhancing global connectivity and trade. Launched in 2013, this multifaceted infrastructure and economic development initiative seeks to revive the ancient Silk Road trading routes by creating a vast network of land and maritime corridors linking Asia with Europe and Africa. This article presents a comprehensive analysis of the impacts and progress of labor138 to date.
Infrastructure Development and Connectivity
One of the key objectives of OBOR138 is to facilitate the construction of modern infrastructure across participating countries. Through extensive investments in roads, railways, ports, and energy projects, China aims to improve regional connectivity and facilitate the movement of goods and services. This approach has led to both positive and negative impacts.
Positive Impacts:
- Enhanced connectivity has bolstered trade between participating countries, fostering economic growth and development.
- Improved transportation networks have reduced logistics costs, making it more cost-effective to move goods between regions.
- Landlocked countries like Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan have gained vital access to sea routes, stimulating their economies.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Some projects have faced delays, cost overruns, and debt sustainability issues, raising concerns about the financial viability of certain initiatives.
- Critics argue that the initiative disproportionately benefits China and raises questions about its geopolitical intentions.
Geopolitical Implications
The scale and scope of OBOR138 have significant geopolitical implications. By investing in strategic locations, China seeks to expand its influence and economic interests. The initiative has led to increased partnerships and engagements with countries across Asia, Africa, and Europe, strengthening China's soft power and diplomatic clout.
Positive Impacts:
- Economic ties fostered by OBOR138 have improved China's relationships with participating countries, leading to potential diplomatic benefits.
- Countries like Pakistan and Sri Lanka have received substantial foreign direct investments, supporting their domestic development efforts.
Challenges and Concerns:
- The initiative has led to heightened geopolitical tensions, particularly with India, which sees some projects in Pakistan as a threat to its sovereignty.
- China's growing economic influence has raised concerns about debt-trap diplomacy and potential loss of economic autonomy for participating countries.
Sustainable Development and Environmental Concerns
OBOR138's extensive infrastructure projects have also raised questions about environmental sustainability and social impacts in the regions involved.
Positive Impacts:
- Green energy projects, such as solar and wind farms, are contributing to the expansion of renewable energy capacity in some participating countries.
Challenges and Concerns:
- Some infrastructure projects have resulted in environmental degradation and displacement of local communities, leading to social unrest and protests.
- The carbon footprint of OBOR138 projects, particularly those involving fossil fuels, may counteract global efforts to combat climate change.
Conclusion
Unraveling the impacts and progress of OBOR138 reveals a complex and multifaceted initiative that is reshaping global trade, connectivity, and geopolitics. While it has brought about positive changes, such as improved infrastructure and economic growth, it also faces challenges related to project implementation, sustainability, and geopolitical tensions. To ensure the long-term success of OBOR138, participating countries and China must work together to address these challenges while fostering an inclusive and sustainable approach to development. Only through joint efforts and mutual cooperation can OBOR138 truly fulfill its potential as a game-changer in the global economic landscape.