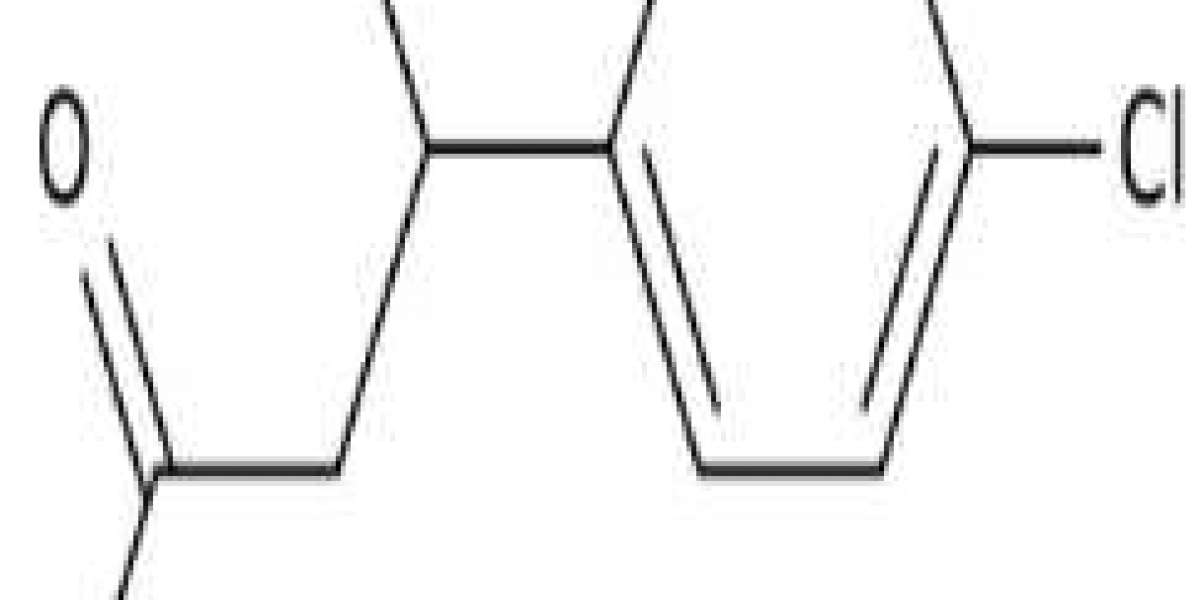
White powder. Melting point: 206-208 °C. Dissolved using hot water, the aqueous solution was neutral, almost insoluble in alcohol, ether, acetone, and other organic solvents, and easily soluble in acidic, alkaline aqueous solutions. The melting point of Chlorobenzene aminobutyric acid hydrochloride: is 179-181 °C. Off-White SolidChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid that is butanoic acid substituted by an amino group at position 4 and a 4-chlorophenyl group at position 3. It acts as a central nervous system dep
Baclofen appears as an odorless or practically odorless white to off-white crystalline powder. (NTP, 1992)|Baclofen is a monocarboxylic acid that is butanoic acid substituted by an amino group at position 4 and a 4-chlorophenyl group at position 3. It acts as a central nervous system depressant, GABA agonist, and muscle relaxant. It has a role as a muscle relaxant, a central nervous system depressant, and a GABA agonist. It is a monocarboxylic acid, a primary amino compound, a member of monochlorobenzenes, and a gamma-amino acid.|Baclofen is a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) agonist used as a skeletal muscle relaxant used for the relief of painful and uncomfortable muscle spasms caused by a variety of conditions. It is known to be particularly useful in treating muscle spasticity associated with spinal cord injury. This drug has recently been studied for the management of alcohol withdrawal, however, a conclusion has not been made regarding baclofen efficacy in this condition, This drug was initially approved by the FDA in 1992. It is available in tablet form, injection form, and powder form (for suspension).|Baclofen is a centrally-acting muscle relaxant commonly prescribed for spasticity in patients with multiple sclerosis. Baclofen has not been linked to rare instances of mild, self-limited, clinically apparent liver injury.|A GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID derivative that is a specific agonist of GABA-B RECEPTORS. It is used in the treatment of MUSCLE SPASTICITY, especially due to SPINAL CORD INJURIES. Its therapeutic effects result from actions at spinal and supraspinal sites, generally the reduction of excitatory transmission.
Reactivity Profile:
Baclofen is an amine. Amines are chemical bases. They neutralize acids to form salts plus water. These acid-base reactions are exothermic. The amount of heat that is evolved per mole of amine in a neutralization is largely independent of the strength of the amine as a base. Amines may be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is generated by amines in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides.
Наука и технология
Related knowledge of Baclofen
Baclofen appears as an odorless or practically odorless white to off-white crystalline powder.