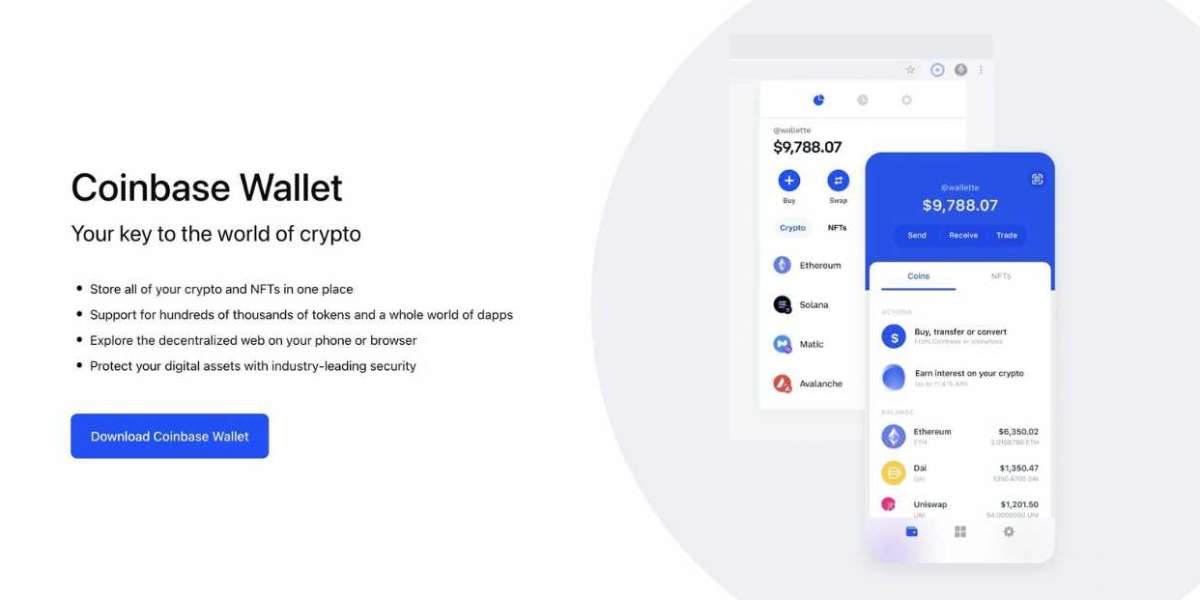
When we talk about technology, we often categorize it into two main types: digital and mechanical. These two categories encompass a vast array of tools, devices, and systems that have revolutionized industries, transformed societies, and reshaped human progress. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the characteristics, applications, and examples of both digital and mechanical technology to provide a deeper understanding of their significance in our modern world.
1. Digital Technology:
Digital technology refers to the use of electronics, computers, and software to process, store, transmit, and manipulate data in the form of binary code (0s and 1s). It has brought about a digital revolution, profoundly impacting various aspects of our lives.
Key Characteristics of Digital Technology:
a. Binary Representation: Digital technology relies on binary code to represent information, where data is expressed as a series of 0s and 1s, making it easily manipulable by electronic devices.
b. High Precision: Digital systems offer high precision and accuracy in data processing and calculations, making them suitable for complex tasks.
c. Scalability: Digital technology is highly scalable, allowing for the efficient handling of vast amounts of data and the ability to expand systems as needed.
d. Flexibility: Digital systems are flexible and adaptable, making it possible to reprogram and update software to meet changing requirements.
e. Connectivity: Digital technology enables devices and systems to connect and communicate with each other over networks, fostering interconnectivity.
f. Reproducibility: Digital data and content can be easily duplicated and shared, making distribution and dissemination efficient.
Applications of Digital Technology:
a. Information and Communication: Digital technology powers the internet, email, social media, and instant messaging, facilitating global communication and information sharing.
b. Computing: Computers and software applications enable data analysis, simulations, modeling, and a wide range of computational tasks.
c. Entertainment: Digital technology drives the entertainment industry, including video games, streaming platforms, digital music, and virtual reality experiences.
d. Healthcare: Electronic health records, medical imaging, telemedicine, and wearable health devices are examples of digital technology applications in healthcare.
e. Finance: Digital technology underpins online banking, electronic payments, cryptocurrency, and algorithmic trading in the financial sector.
f. Education: Digital tools, such as e-learning platforms, online courses, and educational software, have transformed education and remote learning.
Have A Look: How to add roblox gift card
Examples of Digital Technology:
Smartphones: These pocket-sized devices incorporate various digital technologies, including touchscreens, processors, and mobile operating systems, enabling communication, web browsing, and a multitude of applications.
Cloud Computing: Cloud technology allows remote storage and access to data, offering scalability and flexibility for individuals and businesses.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI technologies, including machine learning and natural language processing, are used for automation, predictive analytics, and autonomous decision-making.
Blockchain: This digital ledger technology underpins cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and has applications in secure data recording and smart contracts.
3D Printing: 3D printing technology digitally creates three-dimensional objects layer by layer, revolutionizing manufacturing, prototyping, and even healthcare.
Have A Look: How to convert youtube to mp4
2. Mechanical Technology:
Mechanical technology encompasses devices, machines, and systems that rely on physical mechanisms and principles to perform tasks and accomplish work. It has a long history and continues to be a fundamental part of various industries and sectors.
Key Characteristics of Mechanical Technology:
a. Physical Mechanisms: Mechanical technology operates on physical principles, such as motion, force, energy, and materials, to accomplish tasks.
b. Reliability: Mechanical systems are known for their reliability and durability, often used in critical applications where precision and robustness are essential.
c. Kinematics and Dynamics: Mechanical systems are governed by principles of kinematics (study of motion) and dynamics (study of forces), allowing engineers to design and optimize machines for specific functions.
d. Mechanical Advantage: Mechanical systems often provide a mechanical advantage, amplifying human effort or performing tasks that would be physically challenging or impossible for humans alone.
e. Physical Components: Mechanical technology relies on physical components, including gears, levers, pulleys, and springs, to transmit and transform energy.
Applications of Mechanical Technology:
a. Transportation: Mechanical technology powers vehicles, trains, aircraft, ships, and bicycles, enabling the movement of goods and people.
b. Manufacturing: Mechanical systems are essential in manufacturing processes, including assembly lines, robotics, and machining tools.
c. Construction: Heavy machinery, cranes, bulldozers, and excavators are examples of mechanical technology used in construction and infrastructure development.
d. Energy Production: Mechanical systems, such as turbines, generators, and engines, are used to produce electrical and mechanical energy for various purposes.
e. Healthcare: Medical devices, including surgical instruments, prosthetics, and diagnostic equipment, often incorporate mechanical components.
Examples of Mechanical Technology:
Automobiles: Combining mechanical and electrical components, cars rely on engines, transmissions, and various mechanical systems for propulsion.
Aircraft: Mechanical technology is at the heart of aviation, powering engines, landing gear, control surfaces, and navigation systems.
Industrial Robots: These machines employ mechanical arms and sensors to perform repetitive and precise tasks in manufacturing.
Wind Turbines: Mechanical systems in wind turbines convert kinetic energy from wind into electrical power.
Elevators: Elevator systems use mechanical components to move people and cargo between floors in buildings.
Conclusion
Digital technology and mechanical technology represent two main categories of technological advancements that have significantly shaped our world. Digital technology harnesses the power of electronics and software to process and transmit information, while mechanical technology relies on physical mechanisms to perform tasks and accomplish work. Both types of technology play crucial roles in various industries, and their integration continues to drive innovation and progress in today's interconnected world. Understanding the characteristics, applications, and examples of these technologies is essential for navigating the complexities of our technologically driven society.
Author Bio:
I am a passionate blogger. I love to share my thoughts and ideas through blog posting. Antonio Smith has five years of experience in Tech, Business, Health. I am associated with, thetechnewsmedia.com, thenewtechnologyera.com, digitalmarketingjournals.com, searchenginedesk.com, digibotmedia.com, bloggeroutreachmedia.com, dailynotesjournal.com, edailynotes.com, Gamexspace.com, Countrygamers.com, globalsportsmagazine.com.
Read Also: